Chữ Latinh / Chữ La Mã
Chữ Latinh
|
Chữ Latinh Chữ La Mã | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Thể loại | |
Thời kỳ |
Khoảng năm 700 TCN đến nay |
| Hướng viết | Trái sang phải |
| Các ngôn ngữ | Tiếng Latinh, tiếng Rôman, và tiếng Germanic; phần lớn các ngôn ngữ ở châu Âu; tiếng Việt; tiếng Pali và nhiều ngôn ngữ khác |
| Hệ chữ viết liên quan | |
|
Nguồn gốc |
Chữ tượng hình Ai Cập Chữ La Mã |
|
Hậu duệ | Rất nhiều |
Anh em | Chữ Kirin Chữ Copt Chữ Armenia Chữ Runic/Futhark |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Latn, 215 |
Chữ Latinh, còn gọi là chữ La Mã, là tập hợp bao gồm hai loại chữ cái sau:
- Các chữ cái ban đầu được dùng để viết tiếng Latinh, về sau còn được dùng để viết các ngôn ngữ khác ngoài tiếng Latinh. Phần lớn các chữ cái có trong chữ Quốc ngữ, chẳng hạn như ba chữ cái a, b, c, là chữ cái thuộc loại này.
- Các chữ cái khác được sử dụng kết hợp với các chữ cái thuộc loại đầu. Chữ Quốc ngữ chứa bảy chữ cái thuộc loại thứ hai này là ă, â, đ, ê, ô, ơ, ư.
Chữ Latinh là loại văn tự chữ cái được sử dụng rộng rãi nhất trên thế giới hiện nay.
Lịch sử[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]

Cùng với sự lan rộng của Đế quốc La Mã, chữ Latinh cùng tiếng Latinh cũng mở rộng từ bán đảo Ý sang các vùng lân cận bên bờ Địa Trung Hải. Cho đến cuối thế kỷ XV, chữ Latinh đã phổ biến khắp Tây, Bắc và Trung Âu, chỉ có Đông và Nam Âu vẫn tiếp tục sử dụng chữ Kirin. Ở giai đoạn sau, cùng với quá trình thực dân hóa của các quốc gia châu Âu, chữ Latinh bắt đầu xuất hiện trên khắp thế giới, từ châu Mỹ, châu Đại Dương, châu Phi và một phần châu Á.
Bảng chữ cái Latinh
Nguyên bản bảng chữ cái
| A | B | C | D | E | F | Z | H | I | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | V | X |
| Chữ cái | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tên | ā | bē | cē | dē | ē | ef | gē | hā |
| Cách phát âm (IPA) | /aː/ | /beː/ | /keː/ | /deː/ | /eː/ | /ef/ | /geː/ | /haː/ |
| Chữ cái | I | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q |
| Tên | ī | kā | el | em | en | ō | pē | qū |
| Cách phát âm (IPA) | /iː/ | /kaː/ | /el/ | /em/ | /en/ | /oː/ | /peː/ | /kʷuː/ |
| Chữ cái | R | S | T | V | X | Y | Z | |
| Tên | er | es | tē | ū | ex | ī Graeca | zēta | |
| Cách phát âm (IPA) | /er/ | /es/ | /teː/ | /uː/ | /eks/ | /iː ˈgraika/ | /ˈzeːta/ | |
Bảng chữ cái Latinh mở rộng
Chữ Latinh được điều chỉnh lại cho thích hợp để dùng trong các ngôn ngữ khác, thỉnh thoảng là nhằm thể hiện âm vị không có trong ngôn ngữ khác được viết bằng chữ Latinh. Vì lẽ đó mà người ta tạo ra các cách viết mới để ghi các âm này, thông qua việc thêm dấu phụ lên các chữ cái có sẵn, ghép nhiều chữ cái lại với nhau, sáng tạo ra chữ cái mới hoàn toàn hoặc gán một chức năng đặc biệt do một bộ đôi hoặc bộ ba chữ cái. Vị trí của các chữ cái mới này trong bảng chữ cái có thể khác nhau, tùy thuộc từng ngôn ngữ.
Bảng chữ cái Latinh và tiêu chuẩn quốc tế
Vào khoảng thập niên 1960, các ngành kỹ nghệ máy điện tử và viễn thông ở các quốc gia phát triển đòi hỏi một phương pháp mã hóa ký tự được sử dụng tự do. Tổ chức tiêu chuẩn hóa quốc tế (ISO) đã tóm lược bảng chữ cái Latinh vào tiêu chuẩn ISO/IEC 646 và dựa trên cách sử dụng phổ biến nhằm mục đích phổ biến rộng rãi tiêu chuẩn này.
Do Hoa Kỳ đi trước những bước tiến bộ trong cả hai ngành kỹ thuật và kỹ nghệ trên nên tiêu chuẩn ISO này được xây dựng dựa trên tiêu chuẩn mã trao đổi thông tin Hoa Kỳ (tức ASCII, bộ ký tự dùng cho 26 × 2 chữ cái của bảng chữ cái tiếng Anh).
Về sau, các tiêu chuẩn như ISO/IEC 10646 (Unicode Latinh) vẫn tiếp tục dùng bộ 26 × 2 chữ cái của bảng chữ cái tiếng Anh làm bảng chữ ký Latinh căn bản, đồng thời có mở rộng để giải quyết được những chữ cái trong các ngôn ngữ khác.
| Chữ In // Uppercase Latin alphabet | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chữ Thường // Lowercase Latin alphabet | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x | y | z |
Chữ cái Latinh mới hoàn toàn
Một số ví dụ về chữ cái Latinh mới hoàn toàn so với chữ cái Latinh là các chữ cái wynn ⟨Ƿ/ƿ⟩ và thorn ⟨Þ/þ⟩ của bảng chữ cái Runic, cũng như chữ cái eth ⟨Đ/ð⟩ được thêm vào bảng chữ cái tiếng Anh cổ.
Một số ngôn ngữ Tây, Trung và Nam Phi dùng một vài chữ cái bổ trợ có cách phát âm giống với ký hiệu ngữ âm tương đương trong bảng ký hiệu ngữ âm quốc tế. Chẳng hạn, tiếng Adangme dùng các chữ cái ⟨Ɛ/ɛ⟩ và ⟨Ɔ/ɔ⟩; tiếng Ga dùng ⟨Ɛ/ɛ⟩, ⟨Ŋ/ŋ⟩ và ⟨Ɔ/ɔ⟩. Tiếng Hausa dùng ⟨Ɓ/ɓ⟩ và ⟨Ɗ/ɗ⟩ làm phụ âm hút vào và dùng ⟨Ƙ/ƙ⟩ là phụ âm tống ra.
Multigraph
Một diagraph là một cặp chữ cái dùng để ký một âm hoặc một kết hợp các âm không tương ứng với từng chữ cái theo thứ tự trong cặp chữ đó. Chẳng hạn, tiếng Anh có ⟨ch⟩, ⟨ng⟩, ⟨rh⟩, ⟨sh⟩, tiếng Hòa Lan có ⟨ij⟩ Tương tự, một trigraph là một bộ gồm ba chữ cái ghép lại, chẳng hạn tiếng Đức có ⟨sch⟩, tiếng Breton có ⟨c’h⟩ hay tiếng Milan có ⟨oeu⟩. Trong chính tả của một số ngôn ngữ, diagraph và trigraph được xem là những mẫu tự độc lập trong bảng chữ cái. Vấn đề viết hoa diagraph và trigraph tùy thuộc từng ngôn ngữ, có thể viết hoa chữ đầu tiên mà cũng có thể viết hoa tất cả.
Chữ nối
Chữ nối là một liên hợp hai hay nhiều chữ cái thông thường tạo thành một glyph hoặc một chữ cái mới. Các ví dụ tiêu biểu là ⟨Æ/æ⟩ (bắt nguồn từ ⟨AE⟩, gọi là "ash"), ⟨Œ/œ⟩ (bắt nguồn từ ⟨OE⟩, thỉnh thoảng gọi là "oethel"), ký hiệu viết tắt ⟨&⟩ (từ tiếng Latinh et, nghĩa là "và"), và ký hiệu ⟨ß⟩ ("eszet", bắt nguồn từ ⟨ſz⟩ hoặc ⟨ſs⟩, dạng cổ xưa của chữ s dài ⟨ſ⟩).
Dấu phụ
Dấu phụ là một ký hiệu nhỏ có thể xuất hiện ở một vị trí nào đó ở trên, dưới hoặc ngoài chữ cái, chẳng hạn dấu mũ trong chữ cái ⟨â⟩, ⟨ê⟩, ⟨ô⟩ của tiếng Việt hay dấu umlau trong các chữ cái ⟨ä⟩, ⟨ö⟩, ⟨ü⟩ của tiếng Đức. Chức năng chính của dấu là làm thay đổi cách đọc của chữ cái được gắn dấu nhưng nó cũng có thể làm thay đổi cách phát âm của cả âm tiết hay của chữ, hoặc dấu cũng có thể phân biệt các chữ cùng chữ (cách viết giống hệt nhau nhưng không đồng âm hoặc đồng nghĩa với nhau).
Latinh hóa
Sau giai đoạn các ngôn ngữ dùng chữ Latinh là tiếng Anh, tiếng Pháp, tiếng Tây Ban Nha, tiếng Bồ Đào Nha phổ biến ra toàn cầu nhờ sự trãi rộng của các đế quốc thực dân phương Tây, chữ Latinh đã xuất hiện ở mọi nơi trên thế giới. Các ngôn ngữ hiện không sử dụng phổ biến chữ Latinh để viết như: tiếng Nga, tiếng Ả Rập hay tiếng Trung Quốc thường phải được chuyển tự sang chữ cái Latinh khi được đặt trong văn bản dùng chữ Latinh hay để sử dụng trong môi trường giao tiếp quốc tế. Việc làm này gọi là Latinh hóa hoặc La Mã hóa.
Bảng chữ cái chữ Quốc ngữ
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aa | Ăă | Ââ | Bb | Cc | Dd | Đđ | Ee | Êê | Gg | Hh | Ii | Kk | Ll | Mm | Nn | Oo | Ôô | Ơơ | Pp | Rr | Ss | Tt | Uu | Ưư | Vv | Xx | Yy | |||||
| Aa | Bb | Cc | Dd | Ee | Ff | Gg | Hh | Ii | Jj | Kk | Ll | Mm | Nn | Oo | Pp | Rr | Ss | Tt | Uu | Vv | Ww | Xx | Yy | Zz | ||||||||
Xem thêm
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tham khảo
---------------------------
*

Latin script
|
Latin
Roman
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| Script type | |
|
Time period
|
c. 700 BC – present |
| Direction |
left-to-right
|
| Languages |
Official script in: 132 sovereign states
3 international organizations |
| Related scripts | |
|
Parent systems | |
Child systems |
|
Sister systems | |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Latn (215), Latin |
| Unicode | |
Unicode alias | Latin |
| See Latin characters in Unicode | |
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy (Magna Graecia). The Greek alphabet was adopted by the Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was adopted by the Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet.
The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet, and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet.
Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system[1] and is the most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and Central Europe, most of sub-Saharan Africa, the Americas, and Oceania, as well as many languages in other parts of the world.
Nameedit
The script is either called Latin script or Roman script, in reference to its origin in ancient Rome (though some of the capital letters are Greek in origin). In the context of transliteration, the term "romanization" (British English: "romanisation") is often found.[2][3] Unicode uses the term "Latin"[4] as does the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).[5]
The numeral system is called the Roman numeral system, and the collection of the elements is known as the Roman numerals. The numbers 1, 2, 3... are Latin/Roman script numbers for the Hindu–Arabic numeral system.
ISO basic Latin alphabet
| Uppercase Latin alphabet | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lowercase Latin alphabet | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x | y | z |
The use of the letters I and V for both consonants and vowels proved inconvenient as the Latin alphabet was adapted to Germanic and Romance languages. W originated as a doubled V (VV) used to represent the Voiced labial–velar approximant /w/ found in Old English as early as the 7th century. It came into common use in the later 11th century, replacing the letter wynn ⟨Ƿ ƿ⟩, which had been used for the same sound. In the Romance languages, the minuscule form of V was a rounded u; from this was derived a rounded capital U for the vowel in the 16th century, while a new, pointed minuscule v was derived from V for the consonant. In the case of I, a word-final swash form, j, came to be used for the consonant, with the un-swashed form restricted to vowel use. Such conventions were erratic for centuries. J was introduced into English for the consonant in the 17th century (it had been rare as a vowel), but it was not universally considered a distinct letter in the alphabetic order until the 19th century.
By the 1960s, it became apparent to the computer and telecommunications industries in the First World that a non-proprietary method of encoding characters was needed. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) encapsulated the Latin alphabet in their (ISO/IEC 646) standard. To achieve widespread acceptance, this encapsulation was based on popular usage. As the United States held a preeminent position in both industries during the 1960s, the standard was based on the already published American Standard Code for Information Interchange, better known as ASCII, which included in the character set the 26 × 2 (uppercase and lowercase) letters of the English alphabet. Later standards issued by the ISO, for example ISO/IEC 10646 (Unicode Latin), have continued to define the 26 × 2 letters of the English alphabet as the basic Latin alphabet with extensions to handle other letters in other languages.
Spread
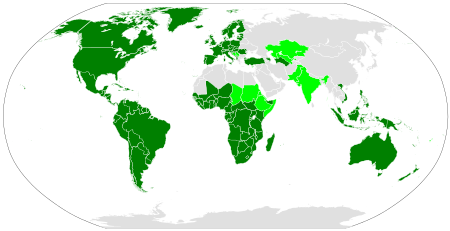
The Latin alphabet spread, along with Latin, from the Italian Peninsula to the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea with the expansion of the Roman Empire. The eastern half of the Empire, including Greece, Turkey, the Levant, and Egypt, continued to use Greek as a lingua franca, but Latin was widely spoken in the western half, and as the western Romance languages evolved out of Latin, they continued to use and adapt the Latin alphabet.
Middle Ages
With the spread of Western Christianity during the Middle Ages, the Latin alphabet was gradually adopted by the peoples of Northern Europe who spoke Celtic languages (displacing the Ogham alphabet) or Germanic languages (displacing earlier Runic alphabets) or Baltic languages, as well as by the speakers of several Uralic languages, most notably Hungarian, Finnish and Estonian.
The Latin script also came into use for writing the West Slavic languages and several South Slavic languages, as the people who spoke them adopted Roman Catholicism. The speakers of East Slavic languages generally adopted Cyrillic along with Orthodox Christianity. The Serbian language uses both scripts, with Cyrillic predominating in official communication and Latin elsewhere, as determined by the Law on Official Use of the Language and Alphabet.[6]
Since the 16th century[edit]
As late as 1500, the Latin script was limited primarily to the languages spoken in Western, Northern, and Central Europe. The Orthodox Christian Slavs of Eastern and Southeastern Europe mostly used Cyrillic, and the Greek alphabet was in use by Greek speakers around the eastern Mediterranean. The Arabic script was widespread within Islam, both among Arabs and non-Arab nations like the Iranians, Indonesians, Malays, and Turkic peoples. Most of the rest of Asia used a variety of Brahmic alphabets or the Chinese script.
Through European colonization the Latin script has spread to the Americas, Oceania, parts of Asia, Africa, and the Pacific, in forms based on the Spanish, Portuguese, English, French, German and Dutch alphabets.
It is used for many Austronesian languages, including the languages of the Philippines and the Malaysian and Indonesian languages, replacing earlier Arabic and indigenous Brahmic alphabets. Latin letters served as the basis for the forms of the Cherokee syllabary developed by Sequoyah; however, the sound values are completely different.[citation needed]
Under Portuguese missionary influence, a Latin alphabet was devised for the Vietnamese language, which had previously used Chinese characters. The Latin-based alphabet replaced the Chinese characters in administration in the 19th century with French rule.
Since the 19th century[edit]
In the late 19th century, the Romanians switched to the Latin alphabet, which they had used until the Council of Florence in 1439,[7] primarily because Romanian is a Romance language. The Romanians were predominantly Orthodox Christians, and their Church, increasingly influenced by Russia after the fall of Byzantine Greek Constantinople in 1453 and capture of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch, had begun promoting the Slavic Cyrillic.
Since 20th century
In 1928, as part of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk's reforms, the new Republic of Turkey adopted a Latin alphabet for the Turkish language, replacing a modified Arabic alphabet. Most of the Turkic-speaking peoples of the former USSR, including Tatars, Bashkirs, Azeri, Kazakh, Kyrgyz and others, had their writing systems replaced by the Latin-based Uniform Turkic alphabet in the 1930s; but, in the 1940s, all were replaced by Cyrillic.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, three of the newly independent Turkic-speaking republics, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, as well as Romanian-speaking Moldova, officially adopted Latin alphabets for their languages. Kyrgyzstan, Iranian-speaking Tajikistan, and the breakaway region of Transnistria kept the Cyrillic alphabet, chiefly due to their close ties with Russia.
In the 1930s and 1940s, the majority of Kurds replaced the Arabic script with two Latin alphabets. Although only the official Kurdish government uses an Arabic alphabet for public documents, the Latin Kurdish alphabet remains widely used throughout the region by the majority of Kurdish-speakers.
In 1957, the People's Republic of China introduced a script reform to the Zhuang language, changing its orthography from Sawndip, a writing system based on Chinese, to a Latin script alphabet that used a mixture of Latin, Cyrillic, and IPA letters to represent both the phonemes and tones of the Zhuang language, without the use of diacritics. In 1982 this was further standardised to use only Latin script letters.
p>With the collapse of the Derg and subsequent end of decades of Amharic assimilation in 1991, various ethnic groups in Ethiopia dropped the Geʽez script, which was deemed unsuitable for languages outside of the Semitic branch.[8] In the following years the Kafa,[9] Oromo,[10] Sidama,[11] Somali,[11] and Wolaitta[11] languages switched to Latin while there is continued debate on whether to follow suit for the Hadiyya and Kambaata languages.[12]21st centuryedit
On 15 September 1999 the authorities of Tatarstan, Russia, passed a law to make the Latin script a co-official writing system alongside Cyrillic for the Tatar language by 2011.[13] A year later, however, the Russian government overruled the law and banned Latinization on its territory.[14]
In 2015, the government of Kazakhstan announced that a Kazakh Latin alphabet would replace the Kazakh Cyrillic alphabet as the official writing system for the Kazakh language by 2025.[15] There are also talks about switching from the Cyrillic script to Latin in Ukraine,[16] Kyrgyzstan,[17][18] and Mongolia.[19] Mongolia, however, has since opted to revive the Mongolian script instead of switching to Latin.[20]
In October 2019, the organization National Representational Organization for Inuit in Canada (ITK) announced that they will introduce a unified writing system for the Inuit languages in the country. The writing system is based on the Latin alphabet and is modeled after the one used in the Greenlandic language.[21]
On 12 February 2021 the government of Uzbekistan announced it will finalize the transition from Cyrillic to Latin for the Uzbek language by 2023. Plans to switch to Latin originally began in 1993 but subsequently stalled and Cyrillic remained in widespread use.[22][23]
At present the Crimean Tatar language uses both Cyrillic and Latin. The use of Latin was originally approved by Crimean Tatar representatives after the Soviet Union's collapse[24] but was never implemented by the regional government. After Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014 the Latin script was dropped entirely. Nevertheless Crimean Tatars outside of Crimea continue to use Latin and on 22 October 2021 the government of Ukraine approved a proposal endorsed by the Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People to switch the Crimean Tatar language to Latin by 2025.[25]
In July 2020, 2.6 billion people (36% of the world population) use the Latin alphabet.[26]
International standards
By the 1960s, it became apparent to the computer and telecommunications industries in the First World that a non-proprietary method of encoding characters was needed. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) encapsulated the Latin alphabet in their (ISO/IEC 646) standard. To achieve widespread acceptance, this encapsulation was based on popular usage.
As the United States held a preeminent position in both industries during the 1960s, the standard was based on the already published American Standard Code for Information Interchange, better known as ASCII, which included in the character set the 26 × 2 (uppercase and lowercase) letters of the English alphabet. Later standards issued by the ISO, for example ISO/IEC 10646 (Unicode Latin), have continued to define the 26 × 2 letters of the English alphabet as the basic Latin alphabet with extensions to handle other letters in other languages.
National standards
The DIN standard DIN 91379 specifies a subset of Unicode letters, special characters, and sequences of letters and diacritic signs to allow the correct representation of names and to simplify data exchange in Europe. This specification supports all official languages of European Union and European Free Trade Association countries (thus also the Greek and Cyrillic scripts), plus the German minority languages.[clarification needed] To allow the transliteration of names in other writing systems to the Latin script according to the relevant ISO standards all necessary combinations of base letters and diacritic signs are provided.[27] Efforts are being made to further develop it into a European CEN standard.[28]
As used by various languages
In the course of its use, the Latin alphabet was adapted for use in new languages, sometimes representing phonemes not found in languages that were already written with the Roman characters. To represent these new sounds, extensions were therefore created, be it by adding diacritics to existing letters, by joining multiple letters together to make ligatures, by creating completely new forms, or by assigning a special function to pairs or triplets of letters. These new forms are given a place in the alphabet by defining an alphabetical order or collation sequence, which can vary with the particular language.
Letters
Some examples of new letters to the standard Latin alphabet are the Runic letters wynn ⟨Ƿ ƿ⟩ and thorn ⟨Þ þ⟩, and the letter eth ⟨Ð/ð⟩, which were added to the alphabet of Old English. Another Irish letter, the insular g, developed into yogh ⟨Ȝ ȝ⟩, used in Middle English. Wynn was later replaced with the new letter ⟨w⟩, eth and thorn with ⟨th⟩, and yogh with ⟨gh⟩. Although the four are no longer part of the English or Irish alphabets, eth and thorn are still used in the modern Icelandic alphabet, while eth is also used by the Faroese alphabet.
Some West, Central and Southern African languages use a few additional letters that have sound values similar to those of their equivalents in the IPA. For example, Adangme uses the letters ⟨Ɛ ɛ⟩ and ⟨Ɔ ɔ⟩, and Ga uses ⟨Ɛ ɛ⟩, ⟨Ŋ ŋ⟩ and ⟨Ɔ ɔ⟩. Hausa uses ⟨Ɓ ɓ⟩ and ⟨Ɗ ɗ⟩ for implosives, and ⟨Ƙ ƙ⟩ for an ejective. Africanists have standardized these into the African reference alphabet.
Dotted and dotless I — ⟨İ i⟩ and ⟨I ı⟩ — are two forms of the letter I used by the Turkish, Azerbaijani, and Kazakh alphabets.[29] The Azerbaijani language also has ⟨Ə ə⟩, which represents the near-open front unrounded vowel.
Multigraphs[edit]
A digraph is a pair of letters used to write one sound or a combination of sounds that does not correspond to the written letters in sequence. Examples are ⟨ch⟩, ⟨ng⟩, ⟨rh⟩, ⟨sh⟩, ⟨ph⟩, ⟨th⟩ in English, and ⟨ij⟩, ⟨ee⟩, ⟨ch⟩ and ⟨ei⟩ in Dutch. In Dutch the ⟨ij⟩ is capitalized as ⟨IJ⟩ or the ligature ⟨IJ⟩, but never as ⟨Ij⟩, and it often takes the appearance of a ligature ⟨ij⟩ very similar to the letter ⟨ÿ⟩ in handwriting.
A trigraph is made up of three letters, like the German ⟨sch⟩, the Breton ⟨c'h⟩ or the Milanese ⟨oeu⟩. In the orthographies of some languages, digraphs and trigraphs are regarded as independent letters of the alphabet in their own right. The capitalization of digraphs and trigraphs is language-dependent, as only the first letter may be capitalized, or all component letters simultaneously (even for words written in title case, where letters after the digraph or trigraph are left in lowercase).
Ligatures
A ligature is a fusion of two or more ordinary letters into a new glyph or character. Examples are ⟨Æ æ⟩ (from ⟨AE⟩, called "ash"), ⟨Œ œ⟩ (from ⟨OE⟩, sometimes called "oethel"), the abbreviation ⟨&⟩ (from Latin: et, lit. 'and', called "ampersand"), and ⟨ẞ ß⟩ (from ⟨ſʒ⟩ or ⟨ſs⟩, the archaic medial form of ⟨s⟩, followed by an ⟨ʒ⟩ or ⟨s⟩, called "sharp S" or "eszett").
Diacritics

A diacritic, in some cases also called an accent, is a small symbol that can appear above or below a letter, or in some other position, such as the umlaut sign used in the German characters ⟨ä⟩, ⟨ö⟩, ⟨ü⟩ or the Romanian characters ă, â, î, ș, ț. Its main function is to change the phonetic value of the letter to which it is added, but it may also modify the pronunciation of a whole syllable or word, indicate the start of a new syllable, or distinguish between homographs such as the Dutch words een (pronounced [ən]) meaning "a" or "an", and één, (pronounced [e:n]) meaning "one". As with the pronunciation of letters, the effect of diacritics is language-dependent.
English is the only major modern European language that requires no diacritics for its native vocabulary[note 1]. Historically, in formal writing, a diaeresis was sometimes used to indicate the start of a new syllable within a sequence of letters that could otherwise be misinterpreted as being a single vowel (e.g., "coöperative", "reëlect"), but modern writing styles either omit such marks or use a hyphen to indicate a syllable break (e.g. "co-operative", "re-elect"). [note 2][30]
Collation
Some modified letters, such as the symbols ⟨å⟩, ⟨ä⟩, and ⟨ö⟩, may be regarded as new individual letters in themselves, and assigned a specific place in the alphabet for collation purposes, separate from that of the letter on which they are based, as is done in Swedish. In other cases, such as with ⟨ä⟩, ⟨ö⟩, ⟨ü⟩ in German, this is not done; letter-diacritic combinations being identified with their base letter. The same applies to digraphs and trigraphs. Different diacritics may be treated differently in collation within a single language. For example, in Spanish, the character ⟨ñ⟩ is considered a letter, and sorted between ⟨n⟩ and ⟨o⟩ in dictionaries, but the accented vowels ⟨á⟩, ⟨é⟩, ⟨í⟩, ⟨ó⟩, ⟨ú⟩, ⟨ü⟩ are not separated from the unaccented vowels ⟨a⟩, ⟨e⟩, ⟨i⟩, ⟨o⟩, ⟨u⟩.
Capitalization
The languages that use the Latin script today generally use capital letters to begin paragraphs and sentences and proper nouns. The rules for capitalization have changed over time, and different languages have varied in their rules for capitalization. Old English, for example, was rarely written with even proper nouns capitalized; whereas Modern English of the 18th century had frequently all nouns capitalized, in the same way that Modern German is written today, e.g. German: Alle Schwestern der alten Stadt hatten die Vögel gesehen, lit. 'All of the Sisters of the old City had seen the Birds'.
Romanization
Words from languages natively written with other scripts, such as Arabic or Chinese, are usually transliterated or transcribed when embedded in Latin-script text or in multilingual international communication, a process termed romanization.
Whilst the romanization of such languages is used mostly at unofficial levels, it has been especially prominent in computer messaging where only the limited seven-bit ASCII code is available on older systems. However, with the introduction of Unicode, romanization is now becoming less necessary. Keyboards used to enter such text may still restrict users to romanized text, as only ASCII or Latin-alphabet characters may be available.
See also
- Western Latin character sets (computing)
- European Latin Unicode subset (DIN 91379)
- Latin letters used in mathematics
- Latin omega
Notes[edit]
- ^ In formal English writing, however, diacritics are often preserved on many loanwords, such as "café", "naïve", "façade", "jalapeño" or the German prefix "über-".
- ^ As an example, an article containing a diaeresis in "coöperate" and a cedilla in "façade" as well as a circumflex in the word "crêpe": Grafton, Anthony (23 October 2006). "Books: The Nutty Professors, The history of academic charisma". The New Yorker.